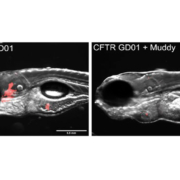
“Mycobacterial Pathogenesis and Novel Therapeutic Targets” team has developed an antibacterial treatment using the Muddy bacteriophage
Laurent Kremer’s team, in collaboration with Graham Hatfull (Pittsbrugh, USA), a specialist in mycobacteriophages, has developed an animal model using zebrafish to test the efficacy of antibacterial treatments on Mycobacterium abscessus, a mycobacterium very similar to those responsible for tuberculosis or leprosy.
Using this model, they demonstrated that a treatment including the bacteriophage Muddy in combination with an antibiotic, rifabutin, resulted in a significant reduction in the infection, the number of abscesses and an increase in the survival of zebrafish embryos infected with M. abscessus.
With the emergence of antibiotic resistance, this old approach based on the use of bacteriophages is once again a promising solution: the efficacy and safety of this approach still need to be validated using contemporary scientific methods.